What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by brief interruptions of breathing during sleep. These episodes usually last 10 seconds or more and occur repeatedly throughout the night. People with sleep apnea will partially awaken as they struggle to breathe, but in the morning they will not be aware of the disturbances in their sleep. The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), caused by relaxation of soft tissue in the back of the throat that blocks the passage of air. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is caused by irregularities in the brain’s normal signals to breathe. The hallmark symptom of the disorder is excessive daytime sleepiness. Additional symptoms of sleep apnea include restless sleep, loud snoring (with periods of silence followed by gasps), falling asleep during the day, morning headaches, trouble concentrating, irritability, forgetfulness, mood or behavior changes, anxiety, and depression. Not everyone who has these symptoms will have sleep apnea, but it is recommended that people who are experiencing even a few of these symptoms visit their doctor for evaluation. Sleep apnea is more likely to occur in men than women, and in people who are overweight or obese

Am I at risk for Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea can affect anyone at any age, even children. Risk factors for sleep apnea include:
- Being male
- Being overweight
- Being over age 40
- Having a large neck size (17 inches or greater in men and 16 inches or greater in women)
- Having large tonsils, a large tongue, or a small jaw bone
- Having a family history of sleep apnea
- Gastroesophageal reflux, or GERD
- Nasal obstruction due to a deviated septum, allergies, or sinus problems
What are the Effects of Sleep Apnea?
If left untreated, sleep apnea can result in a growing number of health problems, including:
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Heart failure, irregular heart beats, and heart attacks
- Diabetes
- Depression
- Worsening of ADHD
- In addition, untreated sleep apnea may be responsible for poor performance in everyday activities, such as at work and school, motor vehicle crashes, and academic underachievement in children and adolescents
- What are the common symptoms of Sleep Apnea ?
- Loud and chronic snoring
- Choking, snorting, or gasping during sleep
- Long pauses in breathing
- Daytime sleepiness, no matter how much time you spend in bed
- Waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat
- Morning headaches
- Restless or fitful sleep
- Insomnia or nighttime awakenings
- Going to the bathroom frequently during the night
- Waking up feeling out of breath
- Forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating
- Moodiness, irritability, or depression
How does the physician determines if I have Sleep Apnea?
Sleep studies are tests that measure how well you sleep and how your body responds to sleep problems. These tests can help your doctor find out whether you have a sleep disorder and how severe it is. Sleep studies are the most accurate tests for diagnosing sleep apnea.
There are different kinds of sleep studies. If your doctor thinks you have sleep apnea, he or she may recommend a polysomnogram (poly-SOM-no-gram; also called a PSG) or a home-based portable monitor.
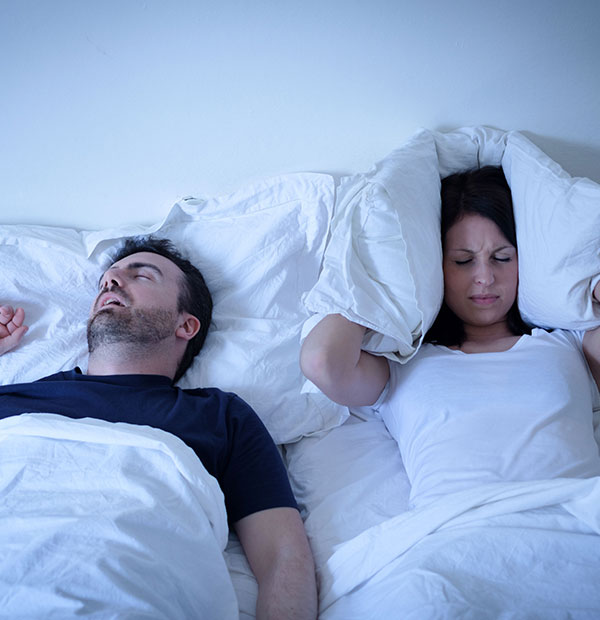

Polysomnogram
A PSG is the most common sleep study for diagnosing sleep apnea. This study records brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and blood pressure.
A PSG also records the amount of oxygen in your blood, air movement through your nose while you breathe, snoring, and chest movements. The chest movements show whether you’re making an effort to breathe.
PSGs often are done at sleep centers or sleep labs. The test is painless. You’ll go to sleep as usual, except you’ll have sensors attached to your scalp, face, chest, limbs, and a finger. The staff at the sleep center will use the sensors to check on you throughout the night.
A sleep specialist will review the results of your PSG to see whether you have sleep apnea and how severe it is. He or she will use the results to plan your treatment.Your doctor also may use a PSG to find the best setting for
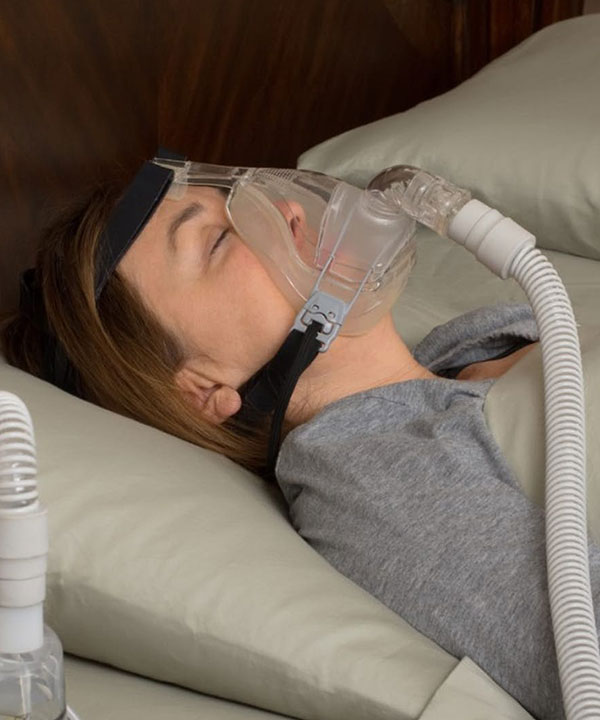
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machine. CPAP is the most common treatment for sleep apnea. A CPAP machine uses mild air pressure to keep your airway open while you sleep.
If your doctor thinks that you have sleep apnea, he or she may schedule a split-night sleep study. During the first half of the night, your sleep will be checked without a CPAP machine. This will show whether you have sleep apnea and how severe it is.
If the PSG shows that you have sleep apnea, you’ll use a CPAP machine during the second half of the split-night study. The staff at the sleep center will adjust the flow of air from the CPAP machine to find the setting that works best for you.
Home-Based Portable Monitor
Your doctor may recommend a home-based sleep test with a portable monitor. The portable monitor will record some of the same information as a PSG. For example, it may record:
- The amount of oxygen in your blood
- Air movement through your nose while you breathe
- Your heart rate
- Chest movements that show whether you’re making an effort to breathe
A sleep specialist may use the results from a home-based sleep test to help diagnose sleep apnea. He or she also may use the results to decide whether you need a full PSG study in a sleep center.
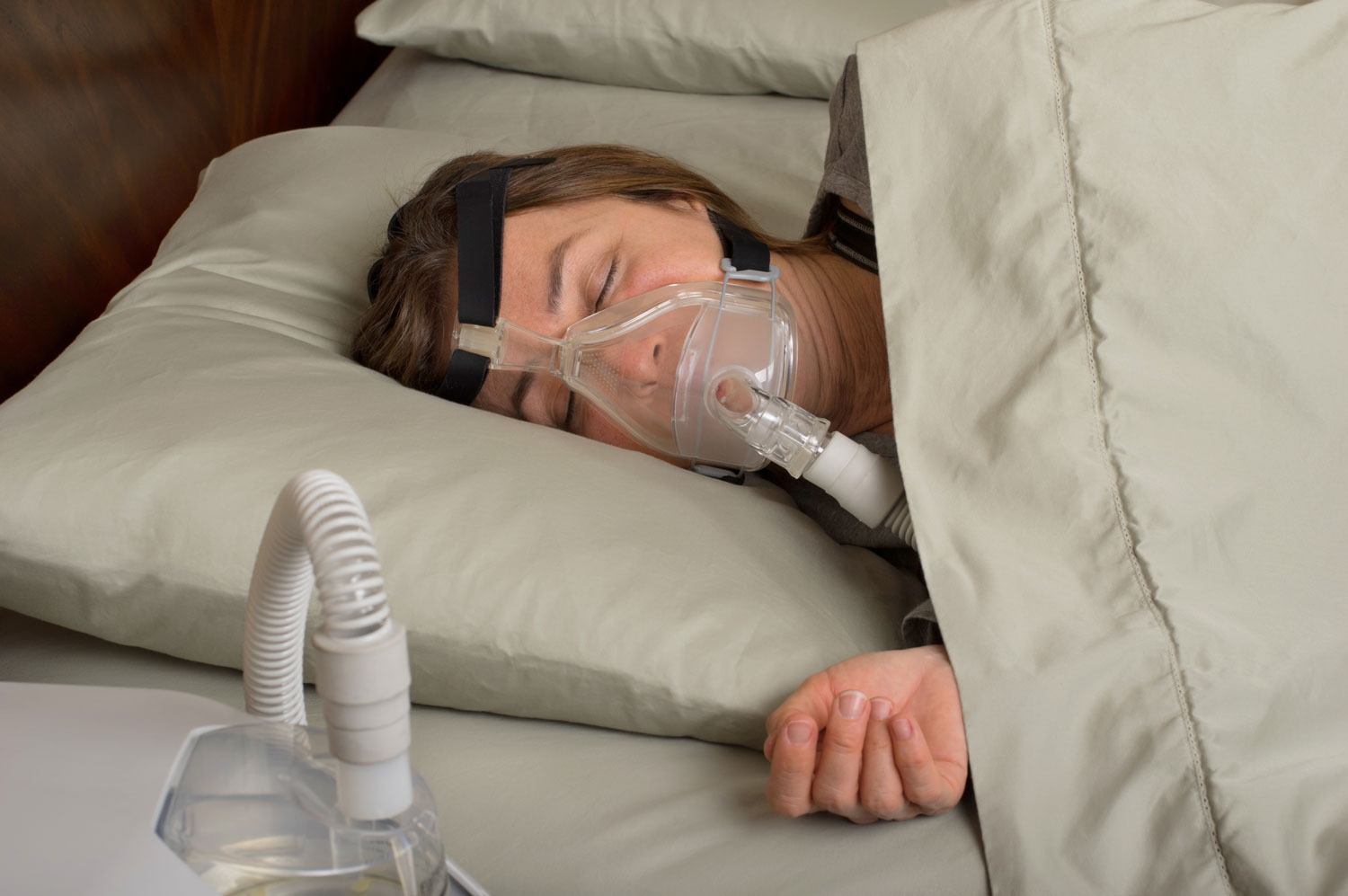

How is Sleep Apnea treated?
Moderate to severe Sleep Apnea is usually treated with a C-PAP (continous positive airway pressure). C-PAP is a machine that blows air into your nose via a nose mask, keeping the airway open and unobstructed. For more severe apnea, there is a Bi-level (Bi-PAP) machine. The Bi-level machine is different in that it blows air at two different pressures. When a person inhales, the pressure is higher and in exhaling, the pressure is lower. Your sleep doctor will “prescribe” your pressure and a home healthcare company will set it up and provide training in its use and maintenance.